Alignment with higher climate neutrality goals
Goal:
The alignment with higher climate neutrality goals aims to ensure that energy efficiency policies and measures are harmonized with the EU’s broader objective of achieving climate neutrality by 2050. This alignment emphasizes reducing greenhouse gas emissions through efficient energy use, fostering a sustainable energy system, and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Objectives:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Implementing energy efficiency measures to significantly lower emissions across various sectors.
- Sustainable Energy Transition: Promoting the use of renewable energy sources and integrating them with energy efficiency initiatives.
- Economic and Social Benefits: Ensuring that the transition to climate neutrality delivers economic benefits, such as job creation and reduced energy costs, and addresses social equity.
- Regulatory and Policy Synergy: Harmonizing national and EU policies to create a coherent and effective regulatory framework supporting climate neutrality.
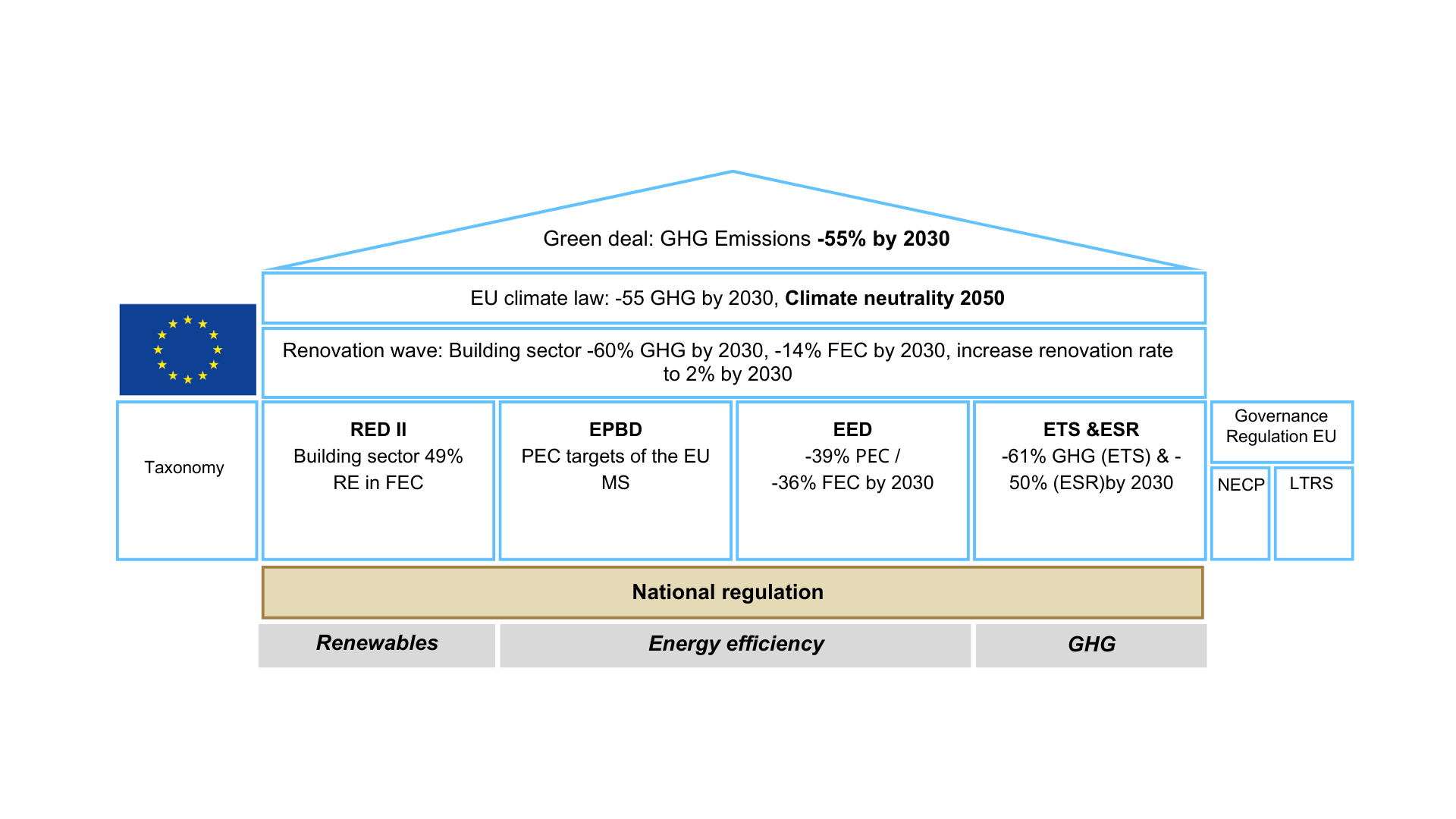 Alignment with climate neutrality goals and its cascading to the European Directives and national regulations
Alignment with climate neutrality goals and its cascading to the European Directives and national regulations
Methodologies or Approaches for Implementation
To align energy efficiency policies with higher climate neutrality goals effectively, the following methodologies and approaches are recommended:
- Integrated Policy Framework:
- Developing comprehensive national energy and climate plans (NECPs) that integrate energy efficiency with renewable energy targets and climate action plans.
- Ensuring consistency and coherence between national regulations and EU directives, such as the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) and the Renewable Energy Directive (RED).
- Sector-Specific Strategies:
- Building Sector: Implementing stringent building codes and standards for new constructions and renovations to ensure high energy performance and integration of renewable energy systems.
- Transport Sector: Promoting the use of electric vehicles (EVs) and improving public transportation systems to reduce emissions.
- Industry Sector: Enhancing energy efficiency in industrial processes through advanced technologies and best practices.
- Innovative Technologies and Solutions:
- Encouraging the adoption of smart grids, energy storage systems, and digitalization to optimize energy use and integrate renewable energy.
- Supporting research and development (R&D) in energy-efficient technologies and their deployment.
- Financial Mechanisms:
- Establishing dedicated funds and financial instruments to support energy efficiency projects and the integration of renewable energy.
- Providing incentives and subsidies for energy-efficient technologies and practices.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Capacity Building:
- Engaging with stakeholders, including policymakers, industry leaders, and the public, to foster collaboration and support for energy efficiency measures.
- Building capacity through training programs and workshops to ensure that professionals are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Integration with EED Goals and Key Elements
The alignment with higher climate neutrality goals supports and is supported by several key elements of the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED):
- Energy Efficiency First Principle: Prioritizing energy efficiency measures ensures that all energy-related decisions consider and implement the most cost-effective and sustainable options first, reducing overall energy demand and emissions.
- Energy Efficiency Targets: Setting ambitious energy efficiency targets aligned with climate neutrality goals drives the adoption of energy-saving measures and supports the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Multiple Benefits of Energy Efficiency: Recognizing the broader benefits of energy efficiency, such as improved air quality, enhanced energy security, and economic savings, reinforces the importance of aligning energy efficiency with climate neutrality goals.
- Heating and Cooling Planning: Effective planning and optimization of heating and cooling systems contribute significantly to reducing emissions and integrating renewable energy sources.
- Exemplary Role of the Public Sector: The public sector can lead by example in implementing energy efficiency measures that align with climate neutrality goals, setting a standard for other sectors to follow.
Aligning energy efficiency policies with higher climate neutrality goals is essential for achieving a sustainable and low-carbon future. By integrating energy efficiency with broader climate action plans, promoting innovative technologies, and ensuring coherent policies, the EU can effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support the transition to a climate-neutral economy by 2050.