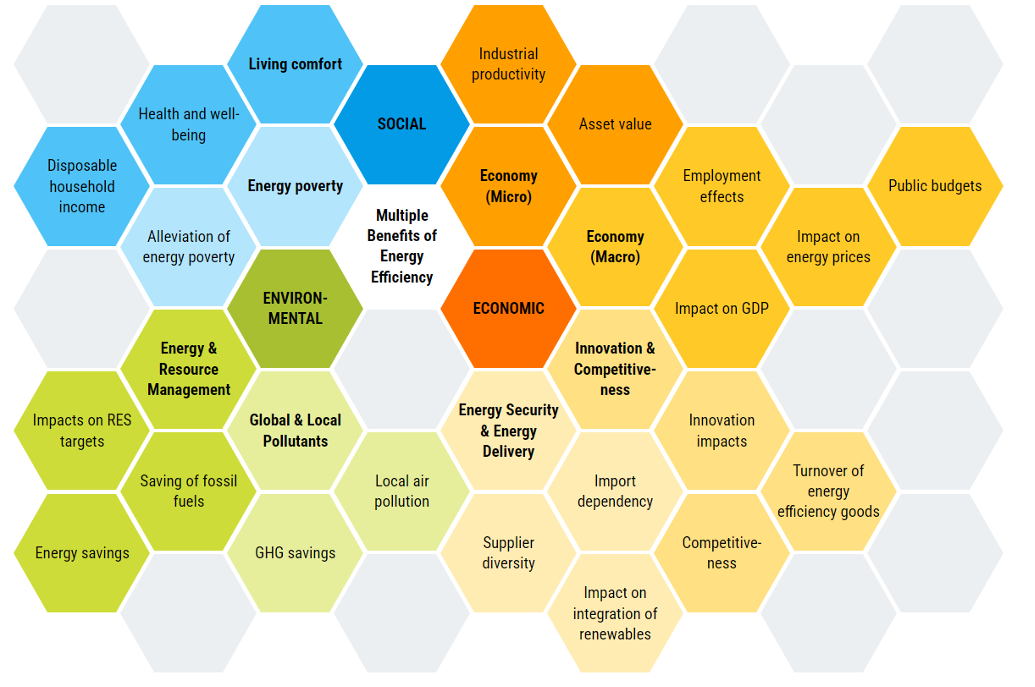
Multiple benefits of energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a cornerstone of sustainable development, offering a wide array of benefits that extend beyond energy savings. These benefits encompass economic, environmental, social, and health aspects, making energy efficiency a key driver for holistic progress. Recognizing and leveraging these multiple benefits is crucial for achieving the EU’s climate and energy goals.
Economic Benefits
- Cost Savings:
- Lower Energy Bills: Reducing energy consumption directly translates into lower energy bills for households, businesses, and public institutions.
- Operational Efficiency: Businesses can achieve significant cost savings through enhanced energy efficiency in their operations, leading to increased competitiveness.
- Job Creation:
- Energy Efficiency Services: The energy efficiency sector, including retrofitting, energy audits, and consulting services, generates employment opportunities.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Promoting energy efficiency facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, creating jobs in the renewable energy sector.
- Economic Growth:
- Investment Attraction: Energy-efficient economies are attractive to investors looking for sustainable and resilient business environments.
- Innovation and Technology Development: Energy efficiency spurs innovation, driving advancements in technology and new business models.
Environmental Benefits
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Energy efficiency measures reduce energy demand, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Compliance with Climate Targets: Energy efficiency supports the EU’s climate targets by reducing emissions across various sectors.
- Resource Conservation:
- Reduced Resource Use: Efficient energy use reduces the need for natural resources, such as fossil fuels, thereby conserving these resources for future generations.
- Sustainable Energy Systems: Energy efficiency promotes the use of renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Improved Air Quality:
- Pollution Reduction: Decreasing energy consumption, particularly from fossil fuels, leads to lower emissions of air pollutants, improving air quality and public health.
Social Benefits
- Energy Security:
- Reduced Dependency: Enhancing energy efficiency decreases reliance on imported energy, improving national energy security and resilience against external shocks.
- Stable Energy Supply: Efficient energy systems are more resilient to supply disruptions, ensuring a stable energy supply for all consumers.
- Improved Living Standards:
- Comfort and Well-being: Energy-efficient homes and buildings provide better thermal comfort, leading to improved living conditions and well-being for occupants.
- Reduced Energy Poverty: Energy efficiency measures can alleviate energy poverty by lowering energy costs for low-income households.
- Health Benefits:
- Indoor Air Quality: Energy-efficient buildings often have better ventilation and indoor air quality, reducing the incidence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Healthier Environments: Lower air pollution levels from reduced energy consumption lead to broader public health benefits.
Integration with EED Goals and Key Elements
The multiple benefits of energy efficiency align with and support the overarching goals of the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) and its key elements:
- Energy Efficiency First Principle: Prioritizing energy efficiency ensures that all decisions consider the broad spectrum of benefits, maximizing positive outcomes for the economy, environment, and society.
- Energy Efficiency Targets: Setting and achieving ambitious energy efficiency targets directly contribute to realizing these multiple benefits, reinforcing the importance of meeting these goals.
- Alignment with Higher Climate Neutrality Goals: The multiple benefits of energy efficiency support the EU’s climate neutrality objectives by reducing emissions and fostering sustainable development.
- Heating and Cooling Planning: Efficient heating and cooling systems provide economic savings, environmental benefits, and improved comfort, demonstrating the multifaceted value of energy efficiency.
- Exemplary Role of the Public Sector: The public sector can showcase the multiple benefits of energy efficiency through its initiatives, setting a precedent for other sectors to follow.
Energy efficiency offers a wide array of benefits that extend beyond mere energy savings. By recognizing and leveraging these multiple benefits, the EU can achieve its climate and energy goals while promoting economic growth, social well-being, and environmental sustainability. Integrating these benefits into policy and decision-making processes is essential for maximizing the positive impacts of energy efficiency initiatives.
Additional resources
- https://www.iea.org/reports/multiple-benefits-of-energy-efficiency/air-quality
- Multiple benefits of energy efficiency investments for financial institutions: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/d30ea98d-03e9-11ed-acce-01aa75ed71a1/language-en
- A comprehensive indicator set for measuring multiple benefits of energy efficiency: https://www.odyssee-mure.eu/publications/archives/multiple-benefits-measure.pdf
- Calculating and Operationalising the Multiple Benefits of Energy Efficiency in Europe: https://combi-project.eu/