Introduction
Modelling is the (iterative) process of framing questions about the real-world in numerical and logical terms, of studying the questions by means of appropriate tools and techniques, of analysing the key outcomes of the studies, and providing insights and information to answer the initial questions and improve the knowledge of the phenomena under investigation.
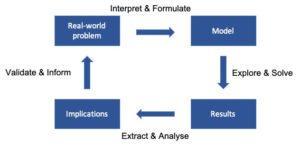 In general, models help capturing and interpreting the complexity of the real world in an understandable form, help analysing and organising large amount of data and information in a structured manner, and help exploring different hypotheses under the same (consistent) framework.
In general, models help capturing and interpreting the complexity of the real world in an understandable form, help analysing and organising large amount of data and information in a structured manner, and help exploring different hypotheses under the same (consistent) framework.
Different real-world problems demand different interpretations, tools, and approaches.
Energy Systems Modelling – to explore future energy systems involving integrated energy and climate policies. This type of models are often used to explore different decarbonisation pathways and the role of each sector (eg power, transportation, building, industry) and each energy form (electricity, natural gas, coal, oil, hydrogen, etc.) in the transition.