Sustainable construction materials
In addition to the sustainable building certification system, Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) are widely used for building construction materials, particularly as most sustainable building certification systems prioritize CO2 as a key indicator, often using CO2 limit values as a foundational criterion. The ISO 14020 series of standards provide globally recognized benchmarks for businesses to develop credible environmental labelling, increasingly vital for products and advertising in response to consumer demand. This includes showcasing the environmental benefits of products, such as the recyclability of packaging, as a core part of a company’s marketing strategy.
ISO 14021 addresses self-declared environmental claims (Type II environmental labelling), providing a framework that enhances the credibility of voluntary claims made by manufacturers, marketers, and resellers for their products or services. The goal of these labels and declarations is to promote products that exert less environmental impact by ensuring the communication of verifiable and accurate information, thereby driving market demand for environmentally responsible products and encouraging continuous improvement. ISO 14024 establishes the requirements for operating ecolabeling schemes, which aim to educate consumers and raise awareness about the environmental impacts of products. Adopted as a benchmark by the Global Ecolabelling Network (GEN), this standard emphasizes the need to consider the entire product life cycle when setting environmental criteria. ISO 14025 outlines the principles and procedures for developing Type III environmental declarations, which provide detailed data on the environmental impacts of products. This standard ensures that the data included in these declarations are independently verified, adding credibility to the environmental performance claims of products. ISO 14064 addresses the monitoring, reporting, and verification of Greenhouse Gases (GHG), relevant for organizations within and outside of regulated schemes like the EU Emission Trading Scheme or the UN CDM mechanism. This standard supports organizations in quantifying and reporting their carbon footprint, thereby demonstrating their commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR). ISO 14067 focuses on the quantification of CO2 emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of products and services, ensuring that these values are comparable on a global scale. This standard integrates the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) principles outlined in ISO 14044, further strengthening the credibility and consistency of CO2 measurement across industries.
Table 1: Different type of eco labelling for materials 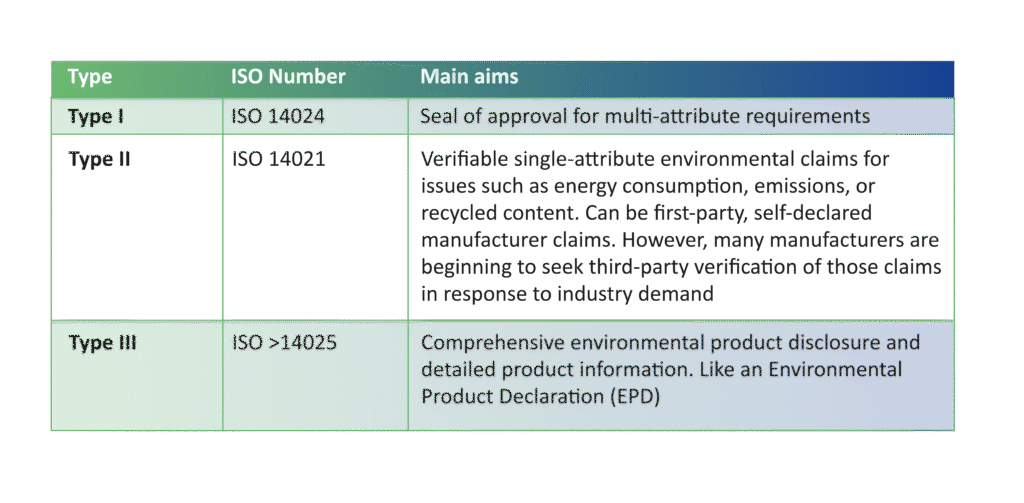 For example, in France, there are seven legally established sustainable building frameworks, incorporating Environmental Product Declarations (EPD), green building certifications, and other sustainability measures. The Netherlands has implemented as well different sustainable building frameworks, underpinned by legislation that mandates the application of LCA. Similarly, Norway utilizes similar sustainable building frameworks, with regulations requiring the integration of LCA in the construction process. For example, Dutch construction law in 2013 already required reports in the form of Life cycle analyses (LCA) according to EN 15804 for all buildings >100m2. LCA calculations should use the national methodology for environmental impact costs. Such a methodology is planned to be applied to infrastructure as well. A unified database has been introduced for the calculation and assessment of the building’s climate impact based on the product EPD climate declarations. The aim is to increase knowledge about the climate impact of building construction and to represent the benefits of climate mitigation.
For example, in France, there are seven legally established sustainable building frameworks, incorporating Environmental Product Declarations (EPD), green building certifications, and other sustainability measures. The Netherlands has implemented as well different sustainable building frameworks, underpinned by legislation that mandates the application of LCA. Similarly, Norway utilizes similar sustainable building frameworks, with regulations requiring the integration of LCA in the construction process. For example, Dutch construction law in 2013 already required reports in the form of Life cycle analyses (LCA) according to EN 15804 for all buildings >100m2. LCA calculations should use the national methodology for environmental impact costs. Such a methodology is planned to be applied to infrastructure as well. A unified database has been introduced for the calculation and assessment of the building’s climate impact based on the product EPD climate declarations. The aim is to increase knowledge about the climate impact of building construction and to represent the benefits of climate mitigation.